By the end of 2016, 100G Ethernet has been widely deployed and becomes a significant portion in data center. Many network-equipment developers are motivated to introduce 100G devices like CFP and QSFP28 modules that consumes as little real estate and power as possible, while achieving necessary price points and delivering superior performance. This post is heading to talk about these two 100G modules and their cabling solutions.
CFP: Out With the Old
Specified by MSA among competing manufacturers, CFP is the first generation 100G transceiver which is designed after the SFP interface, but is significantly larger to support 100Gbps. As we all know, the original CFP has very large size, and in order to meet the need for higher performance and higher density in data center, there is the development of CFP2 and CFP4 specification, which specify a form-factor of 1/2 and 1/4 respectively in size of the original specification. Commonly used CFP/CFP2/CFP4 transceivers are available in 100GBase-SR10 and 100GBase-LR4.
QSFP28: In With the New
QSFP28 is the latest 100G form factor, which is a high-density, high-speed product solution designed for applications in the telecommunications, data center and networking markets. It utilizes four channels of respective signals with data rates up to 25Gbps to meet 100Gbps Ethernet requirement. 100GBase-SR4 and 100GBase-LR4 are two main types of QSFP28 module. The detailed specifications of these two QSFP28s are shown in the following table.
100GBase-SR10 Cabling Solution
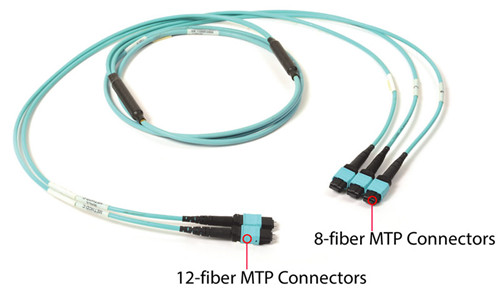
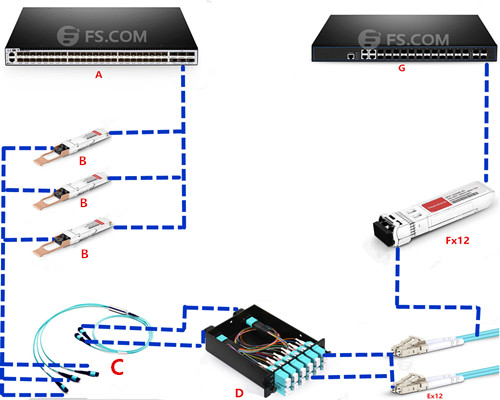
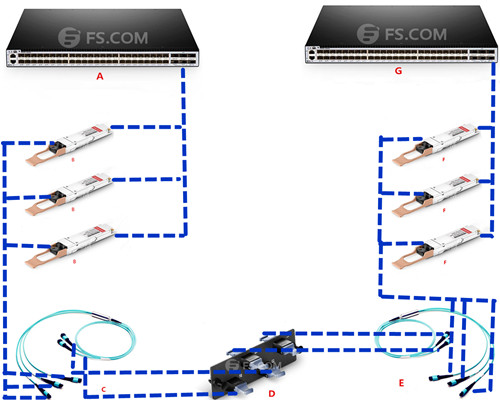
100GBase-SR10 CFP uses a 24 strand MPO cable for connectivity (10 Tx and 10 Rx with each lane providing 10Gbps, leaving 4 channels unused). It can support maximum link length up to 100m and 150m respectively on OM3 and OM4 fiber cable. 100GBase-SR10 can also be used in 10x10 Gigabit Ethernet modes along with ribbon to duplex fiber breakout cables for connectivity to ten 10GBase-SR optical interface.
100GBase-SR4 Cabling Solution
Like 100GBase-SR10, 100GBase-SR4 QSFP28 also uses laser optimized OM3 and OM4 multimode fiber for indication. But 100GBase-SR4 QSFP28 utilizes 12f MPO trunk cable for connectivity (4 Tx and 4 Rx, leaving the middle four unused), which makes it possible to reuse 40GBase-SR4 fiber assemblies when upgrade from 40G to 100G.
100GBase-LR4 Cabling Solution
Both 100GBase-LR4 CFP and QSFP28 are both interfaced with LC connector. They uses WDM technologies to achieve 100G transmission over single-mode duplex LC fiber patch cable supporting the link length up to 10km.
Conclusion
As the need for high bandwidth is increasing, 100G Ethernet will widespread in data center quickly. Equipped with this basic information about 100G modules and their cabling solutions, we will have little worry upgrading to 100G Ethernet.